- abaashishb7
- July 13, 2024
- 10:21 am
- No Comments
Black Hole Sun: Separating Fact from Fiction
Black Hole Sun: Separating Fact from Fiction

Black holes have always fascinated scientists and the public alike. With the iconic song
“Black Hole Sun” by Soundgarden adds a layer of intrigue, it’s easy to see how
misconceptions about black holes can spread. This article aims to demystify black
holes, separate fact from fiction, and explore the concept of a “Black Hole Sun.”

What is a Black Hole?
A black hole is a region in space where gravity is so strong that nothing, not even light,
can escape from it. These cosmic phenomena are formed when massive stars collapse
under their own gravity at the end of their life cycles. The boundary around a black hole
beyond which nothing can escape is called the event horizon.

Historical Background
The concept of black holes dates back to the 18th century with the idea of “dark stars.”
However, it wasn’t until the 20th century that physicists like Karl Schwarzschild and
John Wheeler contributed significantly to our understanding of black holes. Einstein’s
theory of general relativity provided the theoretical framework that predicted the
existence of black holes.
The Song “Black Hole Sun”
“Black Hole Sun,” a song by Soundgarden released in 1994, has become a cultural
Touchstone. While the song’s lyrics are often seen as enigmatic, they contribute to the
public’s fascination with black holes. The song’s title, though poetic, has led to some
curious misconceptions about black holes and their nature.
Common Myths About Black Holes
Myth 1: Black holes are cosmic vacuum cleaners Many people think black holes suck
in everything around them. In reality, a black hole’s gravitational pull operates like any
other object of the same mass. Objects need to come very close to a black hole’s event
horizon to be pulled in.
Myth 2: Black holes can lead to other dimensions This myth is popular in science
fiction. While theoretical physics explores concepts like wormholes, there’s no evidence
that black holes lead to other dimensions. They do, however, distort space and time
around them.
Myth 3: All black holes are the same size Black holes vary significantly in size, from
stellar-mass black holes formed from collapsing stars to supermassive black holes at
the centers of galaxies, which can be millions to billions of times more massive than
the sun.

Black Hole Sun: Scientific Perspective
The idea of our sun becoming a black hole is intriguing but scientifically implausible.
For a star to turn into a black hole, it must have sufficient mass. Our sun lacks the
necessary mass to end its life as a black hole. Instead, it will become a white dwarf
after shedding its outer layers.
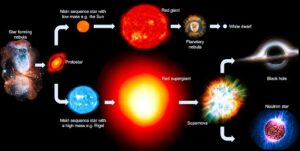
The Lifecycle of Stars
Stars evolve through various stages, from their formation in nebulae to their final
stages as white dwarfs, neutron stars, or black holes. Massive stars, at least 20 times
the mass of our sun, can undergo supernova explosions and collapse into black holes.

Can Our Sun Become a Black Hole?
No, our sun does not have enough mass to become a black hole. It will eventually
become a red giant and then shed its outer layers, leaving behind a dense core called a
white dwarf. this process will happen over billions of years.
Black Hole Sun
Effects of a Hypothetical Black Hole Sun
If the sun were somehow to become a black hole, the gravitational pull at the distance
of Earth’s orbit would remain the same, keeping the planets in orbit. However, without
the sun’s light and heat, life on Earth would not survive, making this a purely
hypothetical and scientifically inaccurate scenario.
Black Holes in Popular Culture
Black holes are a staple of science fiction, appearing in movies like “Interstellar” and TV
shows like “Star Trek.” These portrayals, while often entertaining, can sometimes
perpetuate misconceptions about black holes. For instance, black holes are often
shown as gateways to other dimensions or as cosmic vacuum cleaners, which are not
accurate representations.
Black Hole Sun
Black Hole Research and Discoveries
Recent advancements in black hole research include the first-ever image of a black hole
captured by the Event Horizon Telescope in 2019. This groundbreaking image showed
the black hole at the center of the galaxy M87 and provided visual evidence of the
existence of black holes. Future research aims to understand black hole formation,
growth, and their role in galaxy evolution.

Observing Black Holes
Observing black holes is challenging due to their nature. However, astronomers use
indirect methods, such as observing the behavior of stars and gas clouds near black
holes and detecting gravitational waves from black hole mergers. These methods have
provided significant insights into the characteristics and behavior of black holes.
Black Hole Misconceptions in Media
Media often dramatizes black holes, leading to widespread misconceptions. For
instance, black holes are not roaming space sucking up everything in their path.
Education and accurate representation are essential to dispel these myths and provide a
clearer understanding of black holes and their role in the universe.
The Real Threats from Space
While black holes are fascinating, they are not immediate threats to Earth. Real cosmic
dangers include asteroid impacts and solar flares, which pose more direct risks to our
planet. Understanding these threats and how they compare to black holes helps
prioritize scientific research and public awareness.
Conclusion
Understanding black holes requires separating scientific fact from popular fiction. By
fostering scientific literacy and curiosity, we can appreciate the true wonders of black
holes without falling prey to misconceptions. The concept of a “Black Hole Sun,” while
fascinating, is rooted more in artistic interpretation than scientific reality.
- abaashishb7
- July 13, 2024
- 10:21 am
- No Comments

